The adult chain of survival is a pictorial that outlines the sequence of events that should take place to maximize the chances of survival for a victim. Early initiation of CPR has been shown to increase the probability of survival in case of a cardiac arrest. But before we can start CPR on time, recognizing the cardiac arrest is vital. Each link in chain of survival has been designed to make sure you have some guidance on what to do next. Learn the sequence and save lives.

Adult Chain of survival – in hospital.
When you are in the hospital, you have plenty of resources at your disposal. If you follow the chain of survival, you will increase the chances of survival for the cardiac arrest victim.
- Ideally, prevent a cardiac arrest by having proper protocols in place that identify at risk patients in the hospital and moving them to critical care areas. Identify a cardiac arrest as soon as possible for immediate care delivery.
- If there is a cardiac arrest or sudden deterioration of a patient’s condition (peri arrest), have a code blue activated immediately.
- If you think it’s a cardiac arrest or if you are not sure if you can feel a pulse, assume cardiac arrest and start CPR without waiting for code team to arrive.
- Early use of an AED or defibrillator in case of shockable rhythms (VF or pulseless VT) improves the outcomes. Check the initial rhythm and act on it as soon as possible (You may interrupt CPR to check first rhythm).
- Once you achieve a “Return of spontaneous circulation” – ROSC, it’s important to provide adequate care to prevent a re-arrest. (Explained later in the ACLS course).
- This 6th link has been added as part of 2020 guidelines to emphasize the importance of recovery. The recovery could take a long time and it should not be neglected. (Physiotherapy, psychological support etc)
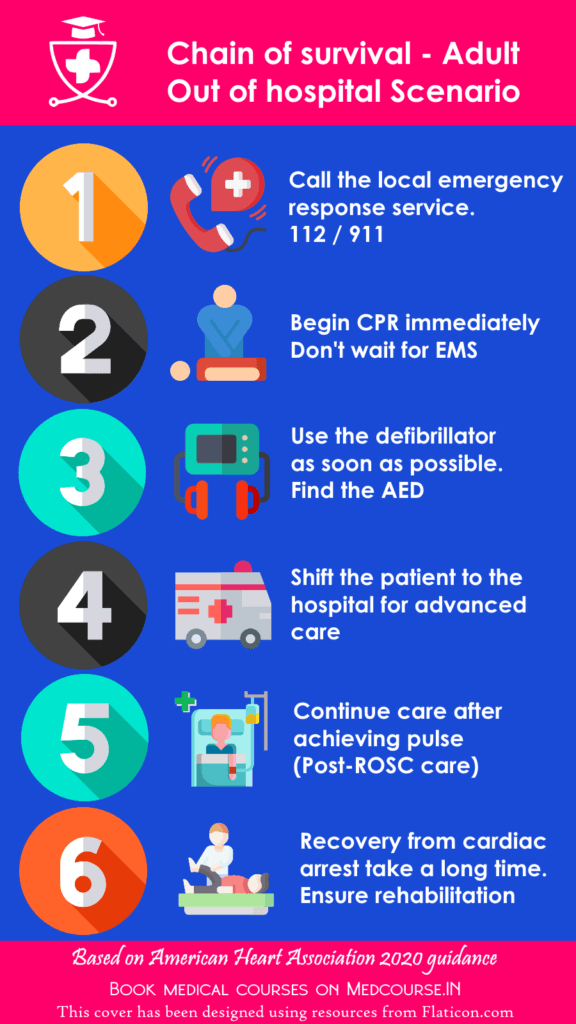
Adult Chain of survival – Out of hospital.
The situation is completely different when the cardiac arrest occurs outside the hospital. You may not have all the resources with you. So, summoning additional help is important in Chain of survival.
- Once you identify a victim that needs help, ask for backup by calling the emergency medical services – EMS. Know your local medical emergency number. Dial 911 in USA ; 112 in India.
- If you think it’s a cardiac arrest or if you are not sure if you can feel a pulse, assume cardiac arrest and start CPR without waiting for EMS team to arrive.
- Early use of an AED or defibrillator in case of shockable rhythms (VF or pulseless VT) improves the outcomes. Find and Automated external defibrillator – AED as soon as possible (You may interrupt CPR to use AED).
- Once the EMS arrives, let them take over and shift the victim to a hospital for advanced care delivery.
- Once you achieve a “Return of spontaneous circulation” – ROSC, it’s important to provide adequate care to prevent a re-arrest. (Explained later in the ACLS course).
- This 6th link has been added as part of 2020 guidelines to emphasize the importance of recovery. The recovery could take a long time and it should not be neglected. (Physiotherapy, psychological support etc)
Every link in the chain of survival has a vital role. Try to pass though each link in a quick manner. Every second is important when you are trying to save a life.
Check the pediatric chain of survival later in this course.
If you want to get certified in BLS from American heart association, please check upcoming workshops in India. Resource to learn First-aid.